Difference between Gigabit switches and 100M switches
 Mar 06,2020
Mar 06,2020
 Harmony
Harmony
Ethernet switches are switches based on Ethernet to transmit data. Ethernet uses a local area network with a shared bus transmission medium. The structure of the Ethernet switch is that each port is directly connected to the host, and generally works in full duplex mode. The switch can connect many pairs of ports at the same time, so that each pair of hosts communicating with each other can transfer data without conflicts like an exclusive communication medium.
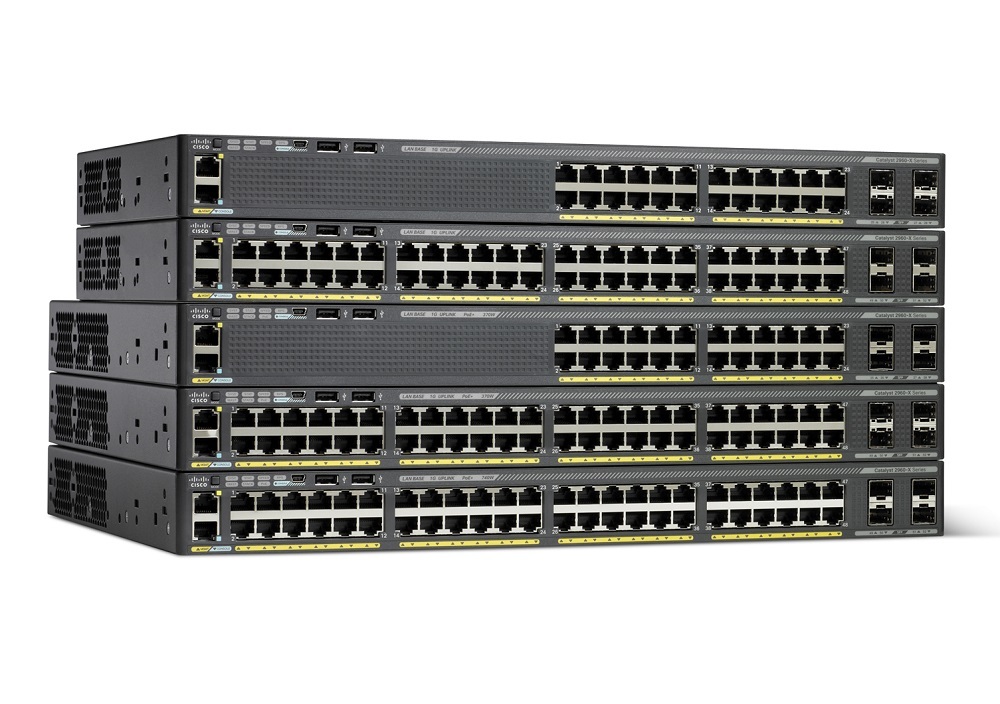

The switch works based on the full-duplex mode, which can upload and download at the same time, without affecting the network performance, and the bandwidth utilization is close to 100%. The theoretical switching speed of a 100M switch is 100Mbps, and the actual transmission volume is about 11MB / S. Gigabit switches have doubled 10 times and are backward compatible with 100M / 10M products.

1. Gigabit faster
In use, Gigabit and 100M are the same, the difference is that Gigabit switches have faster data transmission speed. The downlink ports of 100M switches are all 100M, and the downlink ports of Gigabit switches are all Giga. If two 100M network card users transmit at full speed at the same time, each person using a 100M switch has a transmission speed of about 5MB / S, and each person with a Gigabit switch has a 10MB / S transmission speed.

2. Different application scenarios
For the construction of small networks, high-quality 100M switches can meet the needs. When selecting a small-scale switch, whether the concurrent concurrent operation request can be smoothly operated by the switch chip is the most concerned issue. As more and more services are served on the network, bandwidth guarantee becomes particularly necessary.
 arron@cisco-supplier.com
arron@cisco-supplier.com +86 13599513131
+86 13599513131

 Home
Home Cisco: Top 5 Hot Network Trends in 2020
Cisco: Top 5 Hot Network Trends in 2020  You May Also Like
You May Also Like



 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address


 +86 13599513131
+86 13599513131 arron@cisco-supplier.com
arron@cisco-supplier.com +86 13599513131
+86 13599513131 Rm18e, 27/F, Ho King Comm Ctr, 2-16 Fayuen ST, MongKok Kowloon, Hong Kong
Rm18e, 27/F, Ho King Comm Ctr, 2-16 Fayuen ST, MongKok Kowloon, Hong Kong